

According to this theory, physical exchange of preformed chromatids does not take place. The non-sister chromatids when come in close contact they copy some section of each other resulting in recombination. This theory states that the entire recombinant section or part arises from the newly synthesised section. Breakage and reunion theory to explain the mechanism of crossing over.
This theory remains at present the most accepted explanation for the relationship between genetic crossing over and cytological observed chiasmata.Ĥ. Thus according to this theory each chiasma represents one genetic cross over. The crossing over occurs sometimes during early meiotic stages, perhaps at pachytene, when homologous chromatids are closely paired.Īs the meiotic cell moves towards metaphase and reductional division, a chiasma is formed at the point where crossing over has occurred. According to this theory, first crossing over occurs and then chiasma is formed. This theory was proposed by lanssens and later on elaborated by Belling and Darlington. When two chiasmata are formed, they may involve two, three or all the four chromatids.
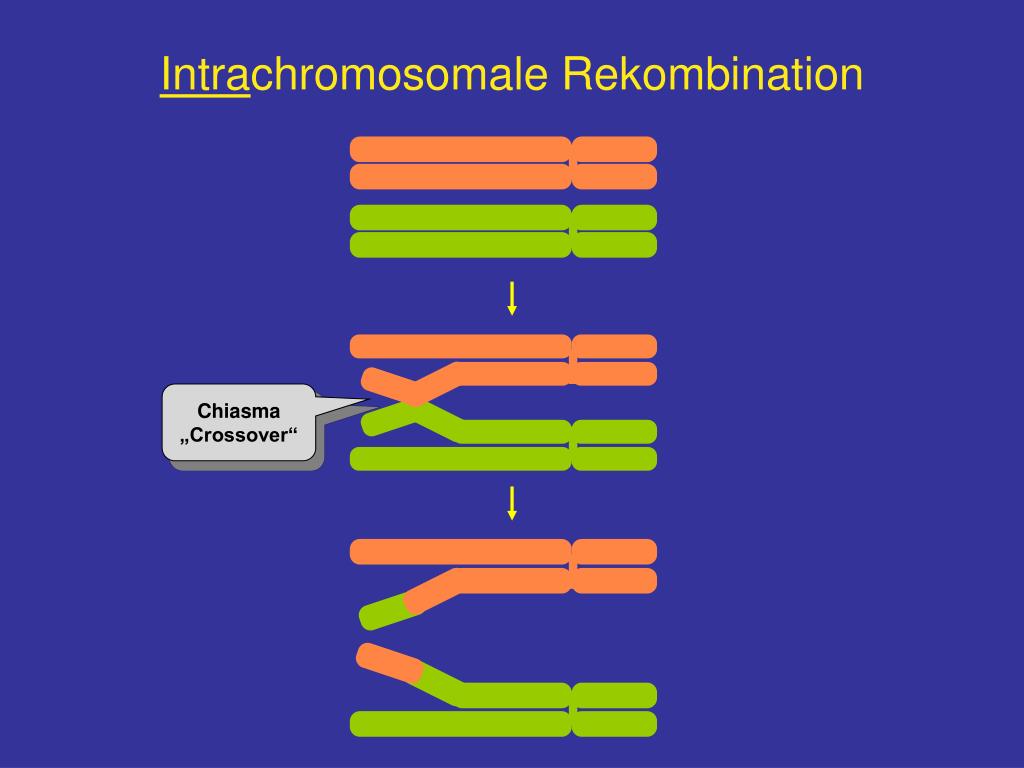
The number of chiasma per bivalent may vary from one to more than one depending upon the length of chromatids. Later on interstitial chiasma is changed to terminal position by the process of chiasmaterminalization. When the chiasma is located at the end of the pairing chromatids, it is known as terminal chiasma and when it is located in the middle part of non-sister chromatids, it is referred to as interstitial chiasma. Depending on the position, chiasma is of two types, viz., terminal and interstitial. Chiasma was first discovered by Janssens in 1909. It is thought to be the place where crossing over takes place.
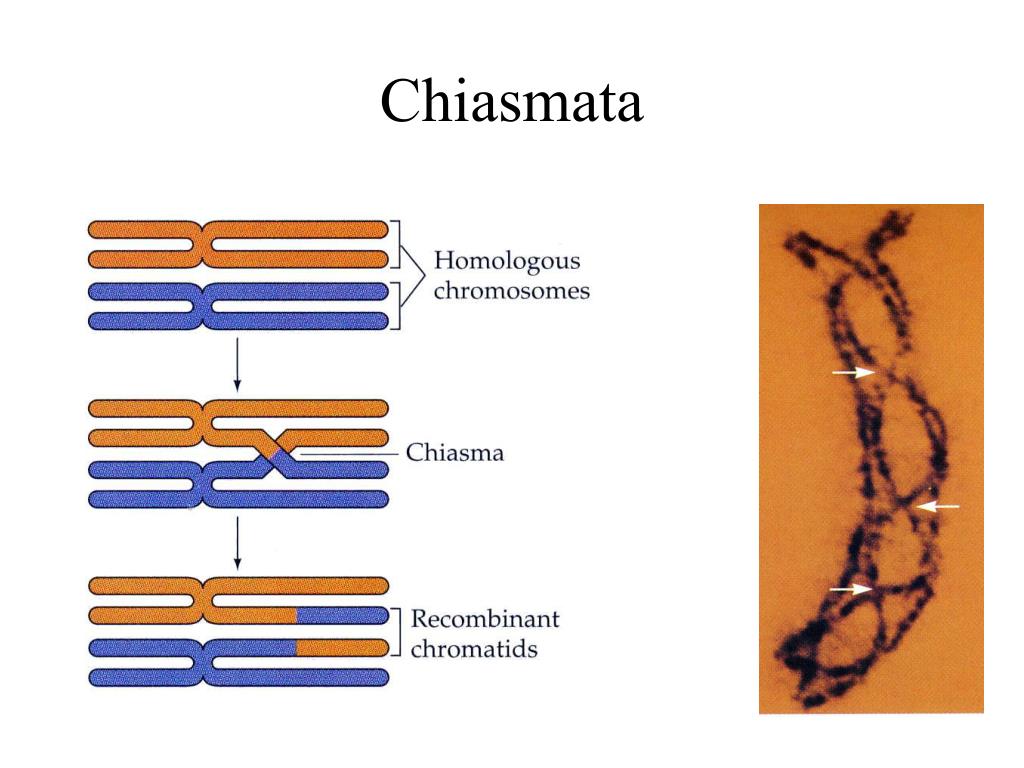
The point of exchange of segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiotic prophase is called chiasma (pleural chiasmata). Crossing over differs from linkage in several aspects (Table 9.1). However, frequency of such cases is extremely low, i.e. Thus,Ĭases of two strand crossing over, somatic crossing over, sister strand crossing over and unequal crossing over are also known. It is expressed as the percentage ratio of recombinants to the total population (recombinants + parental types). The frequency of recombinants can be worked out from the test cross progeny. The value of crossover or recombinants may vary from 0-50%.Ĩ. However, unequal crossing over has also been reported.ħ. Crossing over generally leads to exchange of equal segments or genes and recombination is always reciprocal. Crossing over generally yields two recombinant types or crossover types and two parental types or non-crossover types.Ħ. Crossing over leads to re-combinations or new combinations between linked genes. However, double or multiple crossing over may involve all four, three or two of the four chromatids, which is very rare.ĥ. Each crossing over involves only two of the four chromatids of two homologus chromosomes. It is universally accepted that crossing over takes place at four strand stage.Ĥ. Thus one chromatid from each of the two homologus chromosomes is involved in crossing over.ģ. Crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
